
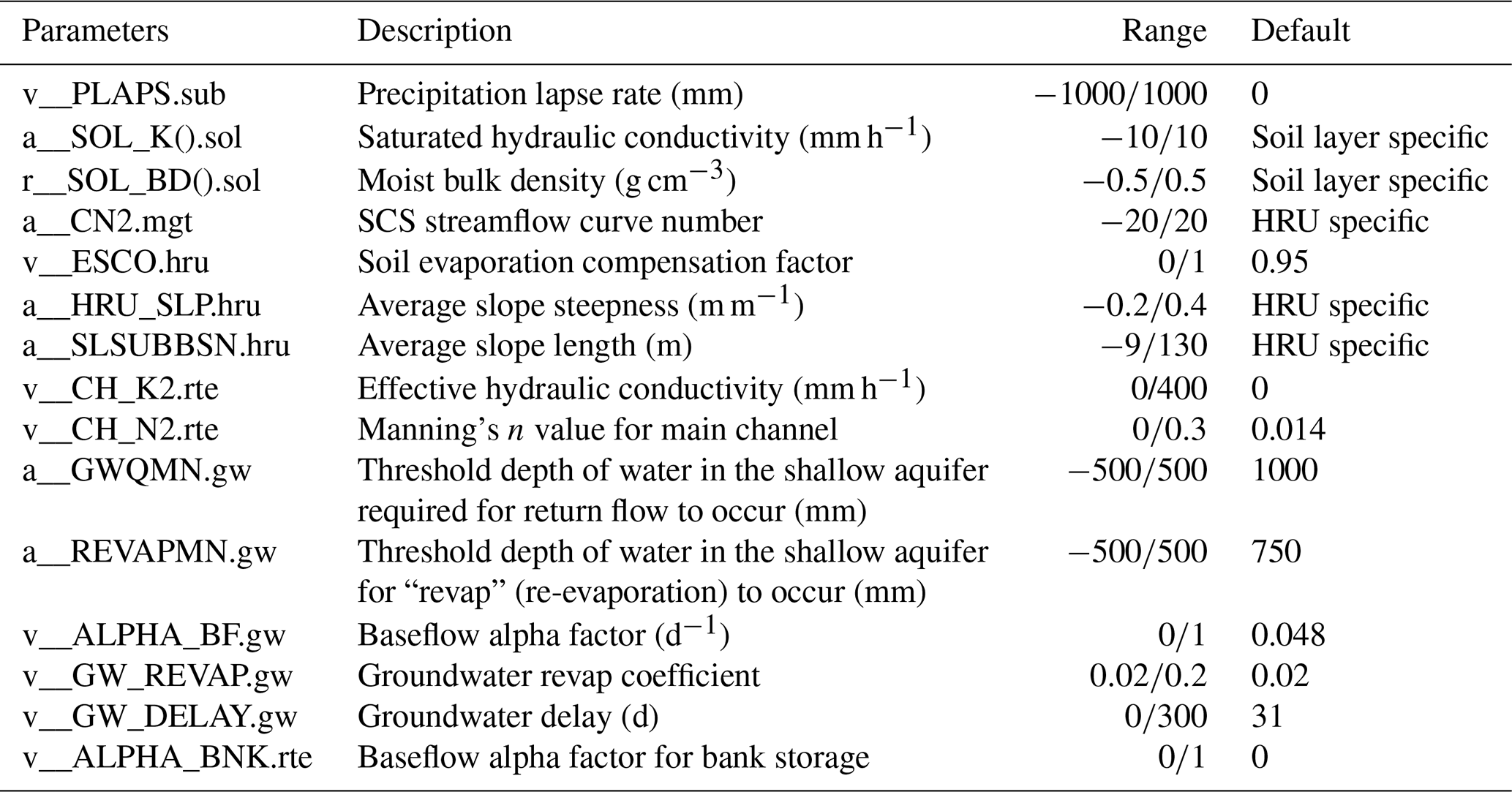
These results showed SWAT’s weakness in predicting monthly peak flows (under estimating). In Wabash River watershed, USA, were evaluated and compared SWAT and DWSM models. Such a direct application of models in different regions where they were developed may be a bad practice. For example SWAT is applied by Reference in Warner Creek watershed, in Big Creek watershed, in Raccoon River watershed and - in different basins of Ethiopia. But, as reported by Reference, models are applied in different regions where they were developed. Hence it may give fairly accurate results if they applied to conditions similar to those from which they were derived. These models are developed for a specific area with the help of statistical observations based on parameters detected in the field. Recently, the most commonly used hydrological models are Hydrological Engineering Centre-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS), Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran (HSPF), Agricultural Non-Point Source (AGNPS), Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), and MIKE SHE. Such selection is highly challengeable for developing country due to shortage of studies that tested the applicability of the models. For a specific watershed, selecting the most suitable hydrological model is necessary to obtain good simulated results and the success hydrologic prediction lies in the proper selection of model input parameters. Ī number of physically-based and distributed watershed models have been developed to model the hydrology of the entire watershed. Today, the watershed models are used to implement an alternative management strategy in the areas of water resources allocation, reservoir siltation, flood control, land use land cove changes and climate change impact assessments. To do so, many computer based models have been developed to simulate the hydrologic processes and the hydrologic effects of different watershed management issues. Modeling of hydrological processes, like rainfall runoff, infiltration, evapotranspiration and groundwater discharge are the most essential tasks to manage the water resources of the basin. Simulated streamflow given by the HEC-HMS model is more satisfactory than that Performance with the R 2 > 0.87 and NSE > 0.73. SWAT gave the model performance with the R 2 > 0.78 and NSE > 0.67 and the HEC-HMS model provided the model Validation indicated that, for river basin Katar, both models could simulateįairly well the streamflow. Were used to evaluate efficiency of the models. Nash-Sutcliffe Error (NSE) and Coefficient of Determination (R 2 ) Both models were calibrated and validated with Performances of these two models were compared in order to select the right Were applied to predict streamflow in Katar River basin, Ethiopia. Models, Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) and Hydrological EngineeringĬentre -The Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS), Necessary to obtain good simulated results. Watershed models have been developed to model the hydrology of the watershed.įor a specific watershed, selecting the most suitable hydrological model is A number of physically-based and distributed


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
